Pulmonary rehabilitation is a topic that has relatively late entered medical practice. Although COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) is one of the first diseases that comes to mind when thinking of pulmonary rehabilitation, it is applicable in many other respiratory diseases as well.
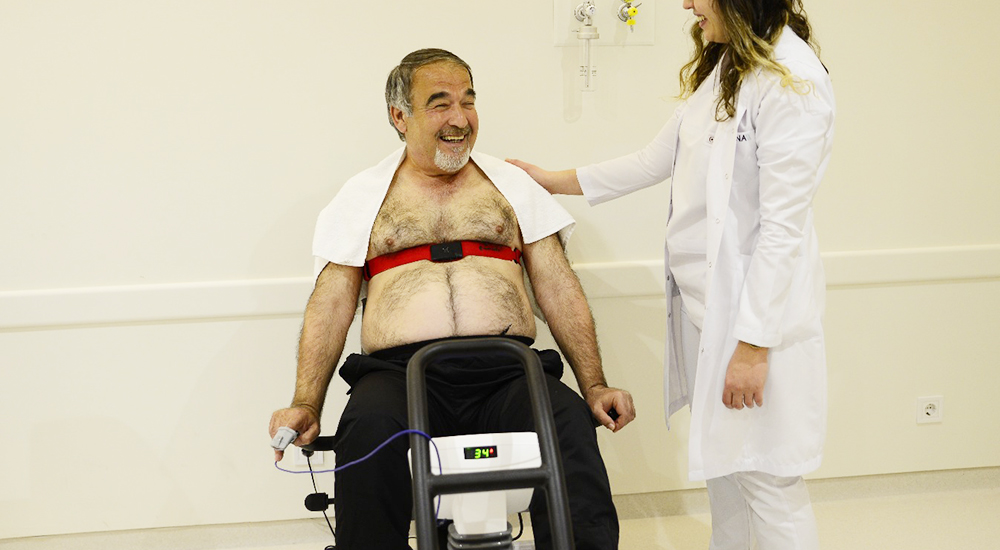
Exercise forms the most important part of pulmonary rehabilitation programs. Exercise improves heart and lung functions, strengthens muscles, and reduces the sensation of breathlessness.
Exercise programs in pulmonary rehabilitation should be tailored to individual needs. Walking, cycling, treadmill (walking band) and other aerobic and strengthening exercises, applied individually or in groups, should be among the primary choices. In addition, respiratory exercises, relaxation techniques, energy conservation methods during daily activities, and methods to reduce breathlessness also constitute other parts of the pulmonary rehabilitation program.
What is Pulmonary Rehabilitation?
Pulmonary rehabilitation can be defined as a treatment method used to help individuals with clinical and/or physiological respiratory diseases maintain their daily personal and life functions at the highest possible level. People with breathing problems tend to limit their physical activities due to fear of developing breathlessness. When physical activity is restricted, strength and endurance decrease. Moreover, the individual’s job satisfaction and level of independence will also decline.
Who is Pulmonary Rehabilitation Applied To?
Exercise programs including endurance (aerobic) and strengthening (resistance) exercises as well as respiratory muscle exercises should be planned. Exercise training should be adapted according to the individual’s needs. Diseases in which pulmonary rehabilitation is applied include:
- Obstructive lung diseases (COPD, asthma, bronchiectasis, cystic fibrosis)
- Restrictive lung diseases (interstitial lung diseases, chest wall diseases, neuromuscular diseases)
- Others (lung malignancies, primary pulmonary hypertension, pre/post cardiac surgery, ventilator-dependent patients, etc.)
What Are the Goals in Pulmonary Rehabilitation Treatment?
- Increasing exercise capacity, muscle strength, and endurance,
- Enhancing compliance with recommended treatments and increasing awareness about lung disease,
- Reducing the severity and frequency of symptoms, thus decreasing dependence on others,
- Maximizing functional and psychological status, increasing motivation,
- Increasing participation in daily life and improving quality of life,
- Controlling the disease and prolonging life expectancy,
- Reducing hospital visits and admissions.
What Are the Exercise Methods Used in Pulmonary Rehabilitation?
- Aerobic (endurance) exercises: These exercises increase vascularization in muscles and increase protein and myoglobin content in muscles. Thus, oxygen distribution in muscle tissue becomes easier. As the aerobic capacity of skeletal muscles increases, improvement in breathlessness is observed. Functional abilities and daily life activities improve, leading to better quality of life. Typically, treadmill, free walking, or cycle ergometer is applied to patients’ lower extremities. These exercises affect large muscle groups.
- Muscle strengthening exercises: These exercises positively affect overall health, improving speed, balance, and coordination. Strengthening of upper arm and back muscles is targeted in this group.
- Upper extremity and shoulder girdle exercises: The muscles in the upper torso, known as the shoulder girdle muscles, also contribute to respiration. Strengthening these muscles with weight exercises improves respiratory function. Exercises such as swimming increase the development of these muscle groups.
- Respiratory muscle exercises: Functional insufficiency in these muscles, especially in COPD and other lung diseases, causes breathlessness and limits exercise capacity. Exercises that increase the strength and endurance of respiratory muscles improve exercise capacity and quality of life. Various methods are used to strengthen respiratory muscles. Respiratory muscle exercises should be applied if symptoms related to airways persist despite peripheral muscle strengthening and endurance exercises.
Besides these exercise methods, many different types of exercises are used in respiratory diseases, all primarily aiming to increase muscle strength and power, especially of the respiratory muscles.
What Are the Benefits of Pulmonary Rehabilitation in COPD Patients?
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs can be combined and applied to COPD patients, significantly improving exercise capacity and muscle strength. Training programs including cycling, stair climbing, and walking should be combined to increase muscle mass and strength. Benefits of pulmonary rehabilitation in COPD patients include:
- Increased exercise capacity,
- Improved quality of life and increased independence,
- Reduced hospital visits and hospital stay durations,
- Decreased anxiety and depression related to COPD,
- Increased muscle strength and endurance.
